The History of Social Security
Social security, since it launched in the US in 1935 under the Old Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance Program, has been part of American retirement planning. The United States is not alone in having social security programs. In fact, the Social Security Administration in collaboration with the International Social Security Association has produced biannual publications highlighting the principal features of social security programs in more than 170 countries. The editions are broken down by regions: Europe, Asia and the Pacific, Africa, and the Americas.
Retirement planning is not a unique issue in the United States. Every country is deciding how they plan to provide for their citizens. Individuals with multiple residencies during their lives are probably the rare individuals who have had to look at multiple country programs. As expected, each country has its own rules for administering the programs. For those interested in some light reading you can find more information here: Social Security Website.
The US program is meant to help citizens with retirement income as early as age 62. Many people choose to delay this income until later in their lives.
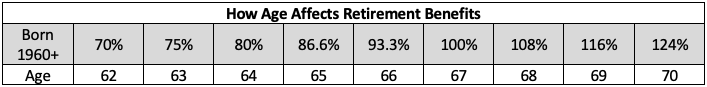
Full retirement for social security in the US now begins at age 67. Below is a helpful chart showing how the age and timing of beginning retirement benefits affect the payout. For instance, if an individual files for benefits at age 62, he or she would receive 70% of the full retirement benefits. In addition, if an individual files for benefits at age 70, he or she would receive 124% of the full retirement benefits.
How Age Affects Retirement Benefits
There is no one filing date that is applicable to everyone. The easiest way to explain this is to operate in the extremes. For example, an unmarried 62-year-old individual who has a terminal illness should file for benefits at 62.
On the other extreme, a healthy unmarried individual who will live well into his or her upper 90’s, who does not need the income to provide for daily lifestyle, and who would stuff put the cash benefits into the mattress, should delay benefits until age 70.
As you can imagine, those two scenarios are rare. Most scenarios are somewhere in the middle. These scenarios require a little more thought and analysis. Some factors to be considered are:
- Current Health
- Projected life expectancy
- Other taxable income
- Total annual cash flow needs
- Overall investment strategy
- Spousal benefits and needs
- Inheritance preferences
Social security is usually not a straightforward decision. In addition, the decision can potentially have a material impact on financial outcomes. Thus, thoughtful discussion and analysis are usually warranted.
